An Electronic System for Summer Training Students Distribution in Organizations with Comparative Study of Association Rule Algorithms
Main Article Content
Abstract
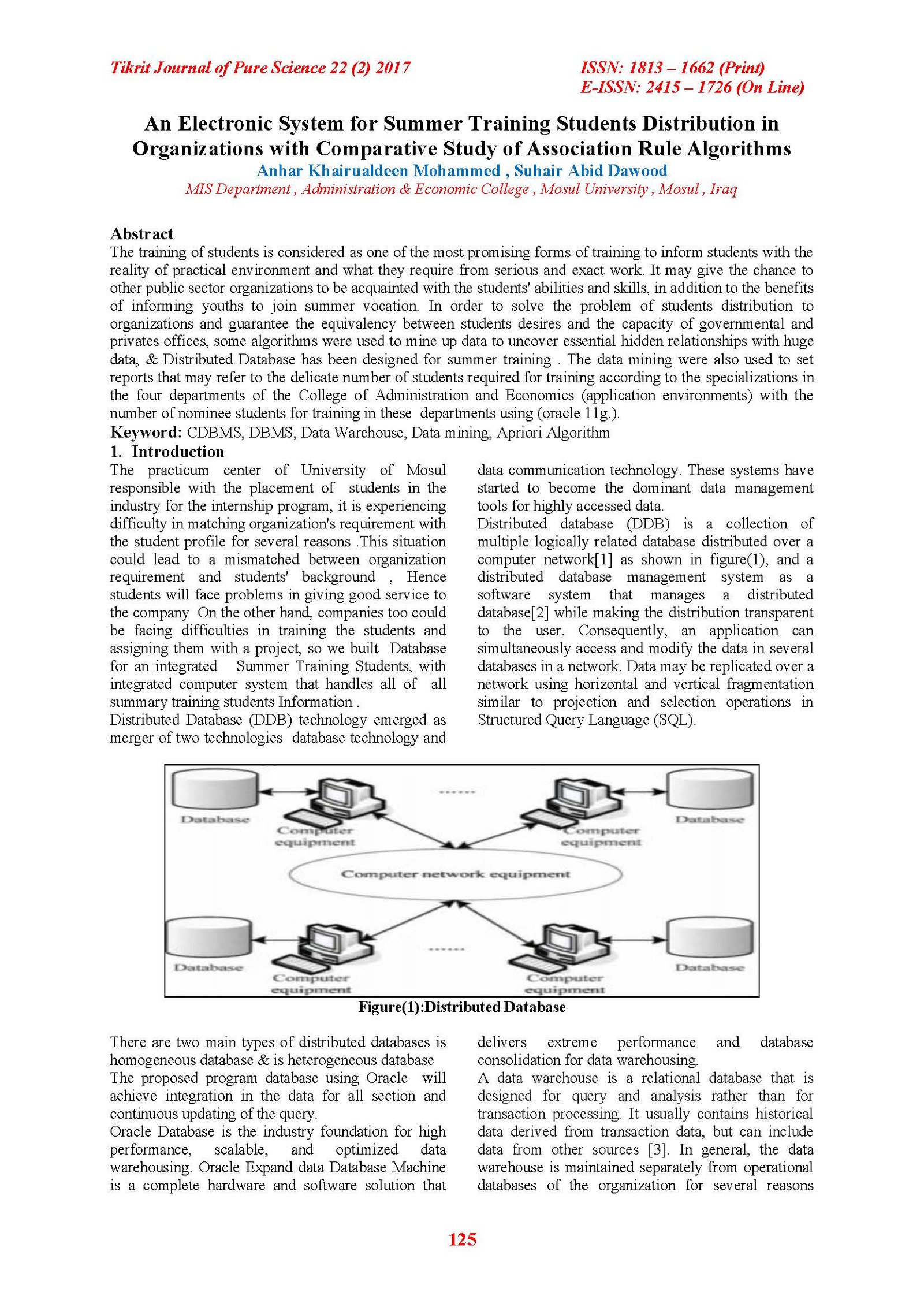
The training of students is considered as one of the most promising forms of training to inform students with the reality of practical environment and what they require from serious and exact work. It may give the chance to other public sector organizations to be acquainted with the students' abilities and skills, in addition to the benefits of informing youths to join summer vocation. In order to solve the problem of students distribution to organizations and guarantee the equivalency between students desires and the capacity of governmental and privates offices, some algorithms were used to mine up data to uncover essential hidden relationships with huge data, & Distributed Database has been designed for summer training . The data mining were also used to set reports that may refer to the delicate number of students required for training according to the specializations in the four departments of the College of Administration and Economics (application environments) with the number of nominee students for training in these departments using (oracle 11g.).
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Tikrit Journal of Pure Science is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which allows users to copy, create extracts, abstracts, and new works from the article, alter and revise the article, and make commercial use of the article (including reuse and/or resale of the article by commercial entities), provided the user gives appropriate credit (with a link to the formal publication through the relevant DOI), provides a link to the license, indicates if changes were made, and the licensor is not represented as endorsing the use made of the work. The authors hold the copyright for their published work on the Tikrit J. Pure Sci. website, while Tikrit J. Pure Sci. is responsible for appreciate citation of their work, which is released under CC-BY-4.0, enabling the unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction of an article in any medium, provided that the original work is properly cited.
References
1. S. K. Verma, Fragmentation Techniques for Distribution Database: A Review, International Journal of Innovative Computer Science & Engineering Volume 3 Issue 2; (2016),PP. 47-50
2. Karanvir Kaur, Ravi Kant Sahu, Query Optimization in Distribution Database, International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and software Engineering,Volume 6,(2016),No.,PP679-684
3. O. Help, Center, Database Data Warehousing Guide,(2014), Oracle and/or its affiliates, p.50
4. W.Mundane, M.Hussein, M.Moukhtar, and F.M.Camino, Intelligent Data Compression Approach in Multidimensional Data Warehouse, International Journal on Computer Science and Engineering, Vol. 3, (2011), No. 2, pp. 951- 960.
5. L.Sapir and S.Armin, A Methodology for the Design of a Fuzzy Data Warehouse, 4th International
IEEE Conference "Intelligent Systems", (2008), IEEE.
6. D. Abadi, P. Boncz, S. Harizopoulos, S. Idreos and S. Madden, “The Design and Implementation of Modern Column-Oriented Database Systems”, Foundations and Trends R in Databases, Vol. 5, (2014),No. 3 ,PP.197–280
7. S.Srinivasan, “ DATA MODELING Applying Relevant Data Modeling Techniques to MPP Columnar Stores - A Point of View”, A Sapient Case Study, (2014), Sapient Corporation,P.30 .
8. A. Bhatia , S. Patil, “Column Oriented DBMS an Approach”, International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks, Vol. 1,(2011), No.2, PP.111-116.
9. http://birtanalytics.actuate.com
10. W. Mcknight, Best Practices in the Use of COLUMNAR DATABASES - How to select workloads for columnar database based on the benefits provided, Calpont,(2011),P.6.
11. G. MATEI,“Column-Oriented Databases, an Alternative for Analytical Environment”, Database Systems Journal Vol. I, (2010), No. 2, PP.3-16
12. J. Celko’s, Analytics and OLAP in SQL”, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers is an imprint of Elsevier, (2006), PP.58-62.
13. A. Khalil, Advanced Database Systems, The American University in Cairo, (2004), Department of Computer Science, p.1.
14. P.Rob, C.Coronel, K.Crockett, Database Systems Design, Implementation &
Management, International Edition,(2008), Edition Cengage Learning EMEA, London, British, P.757.
15. K.Frank , H. A. Dehne, T. Eavis, B. Liang, Compressing Data Cube in Parallel OLAP
Systems. . Data Science Journal, Vol. 6,(2007), PP. 184-197 .
16. B. Jongmuenwai, P. Chinjoho and S.h Prachai, Data Warehouse use Geographic Information System for Ornamentals, Proceedings of the International Multi Conference of Engineers and Computer Scientists(IMECS), Vol I, (2016), Hong Kong, PP 157-162
17. M. Ahluwalia, P. Avril, C, Berger, M. Bird, C. Bruse, et.cl., Oracle Database Licensing Information, 11g Release 2 (11.2),
18. http://www.1keydata.com/datawarehousing/molap-rolap.html, accessed on 3 August (2009).
19. A. Berson, S.j.Smith , "Data Warehousing, Data Mining & OLAP", 1st Edition, (2008), McGraw-Hill, PP. 205-252.
20. M. Wilkie and A. Zaima, ” cubes by design: ROLAP and HOLAP solutions using SAS
and Teradata ", (2009),P.4 http://www.teradata.com/tdmo/v08n03/Tech2Tech/AppliedSolutions/CubesByDesign.aspx accessed .
21. A. Weinberger, M. Ender, “The Power of Hybrid OLAP in a Multidimensional World“, (2000), SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, P.44.
22. A. Parekh, Introduction on Data Warehouse with OLTP and OLAP, International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science, Volume2, (2013), No.8,PP 2569-2573.
23. K. Jayapriya., E. Girija, R.Uma M.C.A, A Technical Review on On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP), International Journal of Computer Science & Communication Networks, Vol.5, (2011), NO.5, PP.315-324
24. S. B. Aher, L.M. Lobo, Data Mining in Educational System uses WEKA, IJCA Proceedings of International conference on Emerging Technology Trends, Foundation of computer science, (2011),New York, USA,P.20
25. B.Marvin, the Impact of Data Imputation Methodologies for Knowledge Discovery, Doctor of Business Administration, (2008),Morehead State University,P.2
26. M.M. Mazid, A. B.Shawkat A. Kevin, S. Tickle, "Finding a Unique Association Rule Mining Algorithm Based on Data Characteristics",5th International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering ICECE , (2008), PP.22-23
27. S.B. Aher, L.M. Lobo, A Comparative study of Association Rule algorithm for course Recommender system in E-learning , International Journal of Computer Applications, Volume 39, (2012),No.1, PP0975-8887
28. M. Mohammed & A. Mohammed, AN IMPROVED APRIORI ALGORITHM FOR ASSOCIATION RULES, International Journal on Natural Language Computing (IJNLC) 0,Vol. 3, (2014),No.1.P.22
29. N.C.Dhande, IDENTIFICATION BEYOND PASSWORD AN ALGORITHMIC APPROACH TO HUMAN MACHINE INTERFACE, IJAIT, Vol. 5,(2013). No. 2, PP.72.
30. T. Scheffer, Finding Association Rules that trade support Optimally Against confidence, in proceedings of the 5th European conference on principles and practice of knowledge Discovery in databases (PKDD'01), (2001),Freiburg, Germany: Springer – Verlag, PP.424-435 .
31. S. Mather ,M. Hall, and E. Frank., using classification to evaluate the output of confidence based association rule mining, Lecture notes in Artificial Intelligence, Advances in artificial intelligence – AI, Berlin, Springer, Vol. 3339, (2004), PP.538-549 .